How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill increasingly in demand, whether for professional photography, recreational flying, or even commercial applications. This guide delves into the intricacies of drone operation, from understanding fundamental regulations and safety protocols to mastering advanced flight techniques and capturing stunning aerial imagery. We’ll explore everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies.
From pre-flight checks and battery management to understanding the nuances of drone controls and camera settings, we aim to provide a clear and accessible path to becoming a proficient drone pilot. We’ll cover essential legal aspects, including licensing and airspace restrictions, ensuring you fly responsibly and within the bounds of the law. This comprehensive guide will equip you with the knowledge and confidence to embark on your drone piloting journey safely and successfully.
Drone Regulations and Safety

Safe and legal drone operation requires understanding and adhering to various regulations and safety protocols. These vary significantly depending on your location, so thorough research is crucial before your first flight.
Drone Licensing and Certification Requirements
Drone licensing and certification vary widely across countries. In some regions, like the United States, recreational drone use might only require registration with the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), while commercial operations necessitate a Remote Pilot Certificate. Other countries may have more stringent requirements, potentially including written exams and flight proficiency demonstrations. Always check with your local aviation authority for specific regulations.
Legal Restrictions on Drone Flight
Numerous restrictions govern where and when you can fly a drone. These often include airspace limitations near airports, restricted airspace around government buildings or military installations, and prohibitions over populated areas or events. No-fly zones are frequently updated, so it’s vital to consult airspace maps and apps before each flight to ensure compliance. Furthermore, many countries have regulations regarding flight altitude and distance from people and property.
Drone Operation Safety Protocols
Prioritizing safety is paramount in drone operation. Pre-flight checks are essential, encompassing battery levels, propeller integrity, GPS signal strength, and overall drone stability. Emergency procedures, including battery failure protocols and safe landing techniques in challenging environments, must be well understood. Always maintain visual line of sight with your drone, and never operate it in adverse weather conditions such as strong winds or heavy rain.
Respect privacy regulations and avoid flying over private property without permission.
Flowchart for Obtaining Drone Operation Permits
The process for obtaining drone operation permits varies by location and purpose. A typical flowchart would begin with identifying your flight purpose (recreational or commercial), followed by determining your location and applicable regulations. This leads to checking for airspace restrictions and registering your drone if required. If commercial use is involved, the flowchart branches to include the process of obtaining the necessary licenses and permits.
Finally, it culminates in confirming all legal requirements are met before flight authorization.
Understanding Drone Components and Controls
Understanding your drone’s components and controls is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will break down the key elements and their functions.
Drone Components
A typical drone comprises several key components working in unison. These include the motors providing thrust, the battery supplying power, the flight controller managing stability and navigation, the GPS module aiding positioning, and the camera capturing images and videos. Additionally, propellers, an airframe, and various sensors contribute to overall functionality.
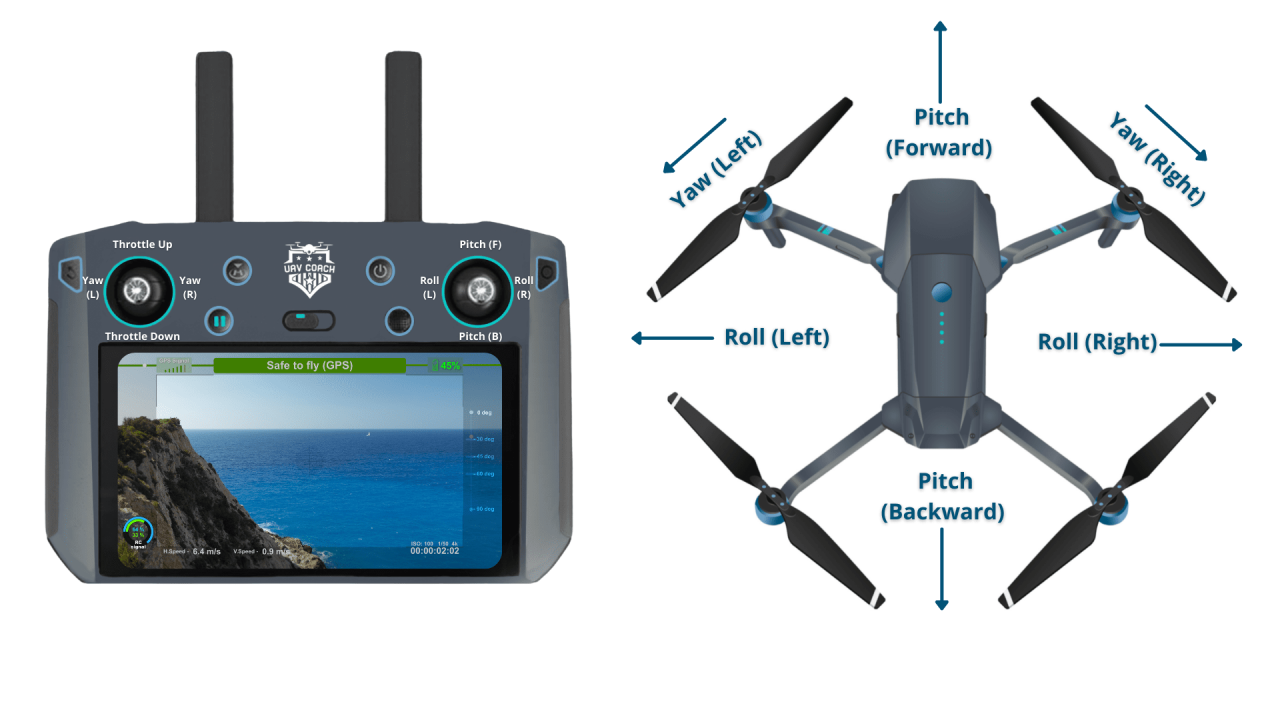
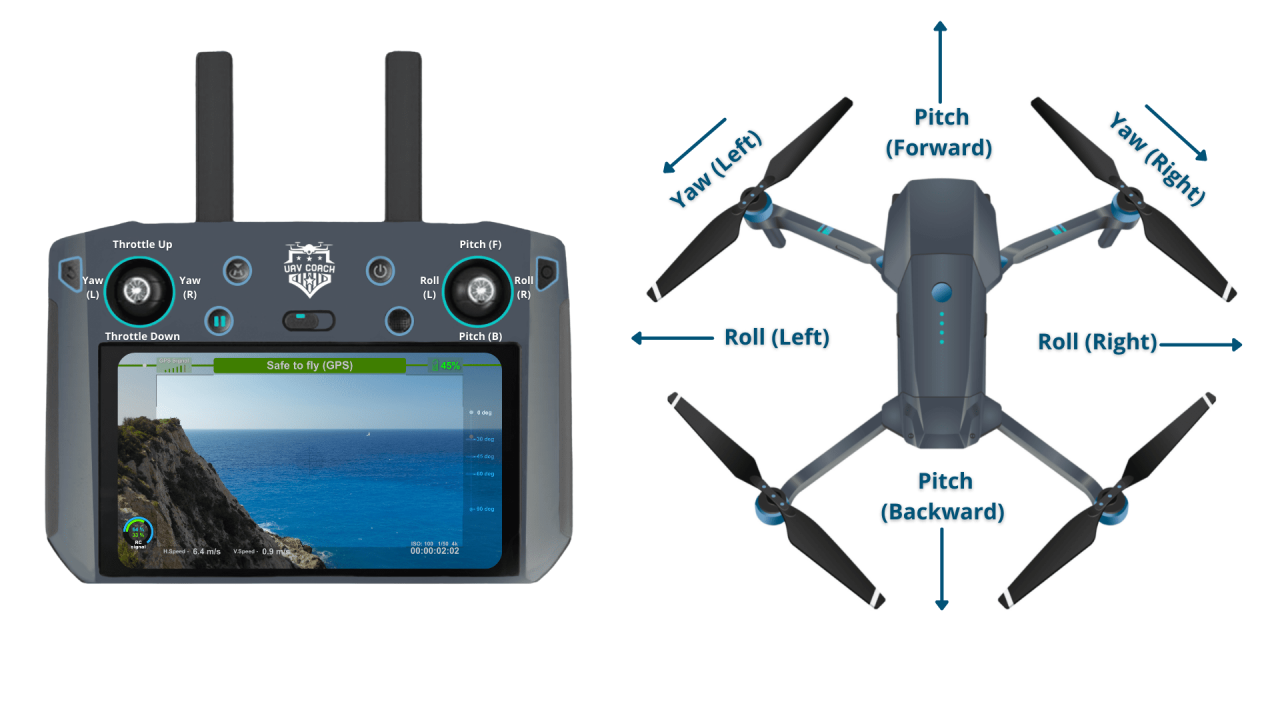
Drone Controller Functions
Standard drone controllers typically utilize two joysticks. One joystick controls altitude and directional movement (forward, backward, left, right), while the other manages yaw (rotation) and camera tilt. Understanding the relationship between joystick movements and drone response is essential for smooth operation.
Types of Drone Controllers
Various drone controllers exist, each offering different features and interfaces. Handheld controllers offer precise control and tactile feedback, while smartphone app controllers provide a more accessible and often user-friendly interface, sometimes with additional features like automated flight modes. The choice often depends on individual preferences and the drone’s capabilities.
Drone Component Specifications
| Component | Specification | Functionality | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motor | Brushless, KV rating (e.g., 2300KV) | Provides thrust for flight | Higher KV generally means higher speed |
| Battery | LiPo, voltage (e.g., 11.1V), mAh (e.g., 5200mAh) | Power source for the drone | Higher mAh means longer flight time |
| Camera | Resolution (e.g., 4K), sensor size, lens type | Captures images and videos | Larger sensor size generally means better low-light performance |
| Flight Controller | Type (e.g., FC2.0), processing power | Manages stability, navigation, and sensor data | More powerful controllers enable more advanced flight modes |
Pre-Flight Procedures and Checks
A thorough pre-flight checklist is crucial for ensuring a safe and successful flight. Neglecting this step can lead to various problems, ranging from minor inconveniences to serious accidents.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics, from pre-flight checks to maneuvering, is crucial for safe and effective operation. For a comprehensive guide on the techniques and best practices involved, check out this helpful resource on how to operate a drone before you take to the skies.
This will ensure you’re well-prepared to handle your drone responsibly and proficiently.
Pre-Flight Drone Inspection Checklist
Before each flight, perform a comprehensive inspection. This includes checking the battery charge level, inspecting propellers for damage, ensuring the GPS signal is strong and stable, confirming camera functionality, verifying the flight controller’s status, and assessing the overall condition of the drone for any visible damage or loose components.
Calibrating Drone Sensors and Gyroscopes
Calibrating sensors and gyroscopes is vital for accurate flight performance. This involves following the manufacturer’s instructions, typically involving a series of specific movements to allow the drone to establish its orientation and baseline readings. Improper calibration can result in erratic flight behavior.
Charging and Maintaining Drone Batteries
Proper battery care is essential for safety and longevity. Always use the recommended charger and follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding charging times and storage. Avoid overcharging or discharging batteries, and store them in a cool, dry place when not in use. Regularly inspect batteries for any signs of damage or swelling.
Common Pre-Flight Problems and Solutions

- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an area with better GPS reception.
- Propeller Damage: Replace damaged propellers.
- Gimbal Malfunction: Check gimbal connections and recalibrate if necessary.
- Flight Controller Errors: Consult the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide or seek technical support.
Drone Flight Techniques and Maneuvers
Mastering basic and advanced flight maneuvers is key to safe and efficient drone operation. This section will cover essential techniques and how to handle unexpected situations.
Successfully operating a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to get started is this comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , covering everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and enjoyable drone operation.
Basic Flight Controls
Basic flight controls include taking off, landing, hovering, and directional movement (forward, backward, left, right). Smooth, controlled inputs are essential to avoid jerky movements or unintended maneuvers. Practice these basics thoroughly before attempting more advanced techniques.
Advanced Flight Maneuvers
Advanced maneuvers include turns, ascents, and descents at varying speeds and angles. These require precise control and understanding of the drone’s responsiveness. Practice in a safe, open area away from obstacles.
Flying in Different Weather Conditions
Wind and rain significantly impact drone stability and control. Strong winds can make it challenging to maintain position and can even cause loss of control. Rain can damage electronic components. Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions.
Recovering from Common Flight Errors
- Loss of Control: Immediately initiate emergency landing procedures.
- Low Battery Warning: Land the drone immediately and safely.
- GPS Signal Interference: Return to a location with a strong GPS signal.
- Propeller Failure: Initiate emergency landing procedures.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos requires understanding your drone’s camera settings and employing effective photographic techniques.
Drone Camera Settings and Their Effects
Drone cameras typically offer adjustable settings like ISO (sensitivity to light), shutter speed (exposure time), aperture (amount of light entering the lens), and white balance (color temperature). Understanding how these settings impact image quality is crucial for achieving desired results. Higher ISO values increase sensitivity but can introduce noise, while slower shutter speeds require more light but can blur moving subjects.
Capturing High-Quality Aerial Photos and Videos
Capturing high-quality aerial media involves careful consideration of lighting, composition, and camera settings. Optimal lighting conditions typically involve soft, diffused light, avoiding harsh shadows. Careful framing and composition create visually appealing images and videos. Smooth camera movements enhance the viewing experience.
Adjusting Exposure, Focus, and Other Camera Parameters
Many drones allow manual control over exposure, focus, and other parameters. Manual control provides greater flexibility and precision but requires a deeper understanding of photographic principles. Automatic modes offer convenience but may not always yield optimal results in all situations.
Tips for Composing Compelling Aerial Shots
Composing compelling aerial shots involves selecting interesting subjects, using leading lines and patterns to guide the viewer’s eye, and choosing appropriate perspectives to enhance the visual impact. Experimentation and practice are key to developing a keen eye for composition.
Post-Flight Procedures and Maintenance: How To Operate A Drone
Proper post-flight procedures and regular maintenance are crucial for extending the lifespan and performance of your drone.
Post-Flight Drone Checklist
After each flight, perform a post-flight inspection. This includes safely storing the batteries, cleaning the drone’s body and propellers, and reviewing flight logs to identify any potential issues. Properly storing the drone in a safe, dry place is also important.
Regular Drone Maintenance Tasks
Regular maintenance includes inspecting propellers, checking motor mounts for looseness, cleaning sensors, and lubricating moving parts as needed. The frequency of these checks depends on the drone’s usage, but a regular schedule helps prevent unexpected issues.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Troubleshooting
Common malfunctions include motor failures, battery issues, and GPS signal problems. Troubleshooting involves systematically checking each component, potentially consulting the manufacturer’s troubleshooting guide or seeking technical support.
Routine Drone Maintenance Schedule
A sample maintenance schedule might involve a daily inspection of the propellers and battery, a weekly cleaning of the drone body and sensors, and a monthly more thorough inspection of all components. Adjust the frequency based on the drone’s usage and environmental conditions.
Drone Flight Simulation and Practice
Drone simulators provide a safe and cost-effective environment to practice piloting skills and learn advanced maneuvers before flying a real drone.
Benefits of Drone Simulators
Simulators allow pilots to practice in a risk-free environment, reducing the chances of accidents and damage to the drone. They offer opportunities to learn advanced techniques and hone reflexes in various simulated conditions without the cost or risk associated with real-world flight.
Popular Drone Simulator Software
Several popular drone simulator software options are available, often offering realistic flight physics and diverse environments. Many simulators support various drone models and controllers, providing a comprehensive training experience.
Improving Piloting Skills with Simulators
Simulators offer structured training modules, allowing pilots to progressively develop their skills. They provide feedback on performance, identifying areas for improvement. Practicing emergency procedures and handling challenging situations in a simulator builds confidence and preparedness for real-world scenarios.
Resources for Finding and Utilizing Drone Simulators
Numerous online resources provide information on selecting and using drone simulators. These resources include user reviews, tutorials, and community forums, offering valuable insights and support to new and experienced pilots.
Drone Photography and Videography Techniques
Advanced techniques elevate aerial photography and videography from simple snapshots to compelling visual storytelling.
Advanced Aerial Photography and Videography Techniques, How to operate a drone
Advanced techniques include utilizing specific flight paths to create dynamic visuals, such as circular movements around a subject or smooth tracking shots following a moving object. Mastering these techniques significantly enhances the storytelling capabilities of aerial media.
Using Drone Flight Paths and Camera Movements
Careful planning of flight paths and camera movements is crucial for creating dynamic and engaging visuals. Pre-planning these elements helps ensure smooth transitions and avoids jerky or jarring camera movements.
Importance of Lighting and Composition
Proper lighting is essential for high-quality aerial photography and videography. Golden hour (sunrise and sunset) often provides the most appealing light. Careful composition, including the use of leading lines, rule of thirds, and other compositional techniques, improves the visual appeal of the final product.
Examples of Aerial Shots
- Establishing Shots: Wide shots that provide context and orientation.
- Close-ups: Detailed shots highlighting specific features or subjects.
- Tracking Shots: Smooth shots following a moving subject.
- Aerial Panoramas: Stitched images creating wide, panoramic views.
- Vertical Shots: Shots looking directly down, emphasizing perspective.
Mastering the art of drone operation involves a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical skill. By understanding drone regulations, familiarizing yourself with the technology, and practicing safe flight techniques, you can unlock the immense potential of aerial exploration. This guide has provided a foundation for your journey; now it’s time to take flight, capture breathtaking visuals, and responsibly explore the world from a unique perspective.
Remember to always prioritize safety and adhere to local regulations.
FAQ Insights
What is the best drone for beginners?
Several user-friendly drones are ideal for beginners, often featuring features like GPS stabilization and automatic return-to-home functions. Research models with good reviews and consider your budget.
How long does a drone battery last?
Drone battery life varies greatly depending on the model, usage (e.g., hovering vs. active flight), and weather conditions. Check your drone’s specifications for estimated flight times.
What should I do if I lose control of my drone?
If you lose control, prioritize safety. If equipped, use the return-to-home function. If not, try to guide it down gently. Contact local authorities if it poses a hazard.
Can I fly my drone anywhere?
No. Drone flight is heavily regulated. Check local and national airspace restrictions before flying. Prohibited areas often include airports, military bases, and crowded events.
